Diabetes mellitus (lat. Diabetes mellitus) is a chronic, incurable systemic metabolic disorder characterized by a persistently high level of glucose in the blood. This is mainly due to hereditary factors and due to reduced secretion or reduction of the biological effects of the hormone insulin or their combination. This deficiency interferes with the metabolism of carbohydrates, fats and proteins in the body (which manifests itself in typical problems), and after a long period of time it affects the structure and function of blood vessels, nerves and other vital organs and organ systems.
Diabetes is one of the most common endocrine disorders with a constant increase in prevalence (especially in developed countries). It is the result of a modern lifestyle and an increase in the number of external etiological factors, among which obesity stands out.
Diabetes is most common in the elderly as a result of generalized degenerative and sclerotic changes in the body (affecting the pancreas), and in younger adult men and women it may be associated with genetic disorders or damage to the pancreas as a result of certain infectious diseases. diseases.
Types of diabetes
Due to the different clinical picture, there are several forms (types) of diabetes today:
- Diabetes in childhood (from 0 to 14 years)
- Juvenile diabetes (from 15 to 24 years)
- Adult diabetes (25 to 64 years)
- "senile" diabetes (from 65 to the end of life)
Expert doctors classify diabetes in their own way:
- Endocrine diabetes, combined with diseases of the endocrine glands (endocrine glands).
- Pancreatogenic diabetes associated with diseases of the pancreas (diabetes).
- Iatrogenic diabetes, which occurs in children after the use of certain types of drugs.
- Hepatic (hematogenous) diabetes mellitus, in patients with liver failure and other diseases.
Type 1 diabetes (insulin dependent)
Type 1 diabetes is the most severe form of diabetes and occurs because the cells of the pancreas (beta cells) produce very little or no insulin. It can occur at any age, but is most common in children and young adults. Insulin is administered from the first day. Strict self-control, diet and physical activity are a mandatory part of treatment. You can read more about insulin therapy in the article about insulin.
type 2 diabetes
Type 2 is the most common form of diabetes here and around the world. The pancreas of patients of the other type produces insulin, but in insufficient quantities, or the body creates resistance (immunity) to the hormone insulin. It occurs at all ages, but most often in adults (over 40), obese and elderly people. The modern way of life with a high daily pace is very suitable for the development of this type of diabetes. Treatment is diet or a combination of diet and oral antidiabetic drugs. Herbal teas are used as an aid in all cases of moderate physical activity. If this therapy does not show positive results, they switch to insulin therapy, with the possibility of using oral antidiabetic drugs.
Diabetes during pregnancy (gestational)
This latent form of diabetes is associated with pregnancy, during which there is a change in the hormonal balance in women, which can lead to disruption of insulin secretion and, consequently, an increase in blood glucose levels. The risk group includes women over the age of 25 who were overweight before pregnancy, especially those with a genetic predisposition to developing the disease. Blood sugar levels usually stabilize after the baby is born. However, in women, gestational diabetes can later lead to type 2 diabetes.
Symptoms of diabetes
Symptoms of diabetes are often invisible. The first signs of diabetes, especially type 2, may seem minor and harmless, if they appear at all. You can have diabetes for months or even years without seeing any signs.
Understanding the possible symptoms of diabetes can lead to early diagnosis and treatment. If you have any of the following signs and symptoms, contact your doctor immediately.
- Excessive thirst and frequent urination are classic signs and symptoms of diabetes. When he is sick, excess sugar (glucose) accumulates in the blood. Your kidneys have to work hard to filter and absorb excess sugar. If your kidneys fail, the excess sugar is excreted in the urine as a fluid from the tissues. This causes more frequent urination, which can lead to dehydration. You will want to drink more fluids to quench your thirst, which again leads to frequent urination.
- Fatigue can be caused by many factors. It can also be caused by dehydration, frequent urination, and the body's inability to function properly because less sugar can be used for energy.
- Weight loss is also recognized as a possible sign and symptom of diabetes. When you lose sugar through frequent urination, you lose calories. At the same time, diabetics can get sugar from food for cells, which leads to constant hunger. The overall effect is potentially rapid weight loss, especially if you have type 1 diabetes.
- Symptoms of diabetes can sometimes include vision problems. High blood sugar draws fluid from tissues, including the eyes. This affects the ability to concentrate. If left untreated, diabetes can lead to eye damage. For most people, these early changes do not cause vision problems. However, if these changes do not last for a long time, they can lead to vision loss and blindness.
- Slow wound healing or frequent infections. Doctors and patients have noticed that infections are more common if you have diabetes. Scientists, however, have not yet been able to explain the reason for this. High blood sugar levels may impair natural wound healing and the ability to fight infection. Bladder and vaginal infections are particularly common in women.
- Tingling in hands and feet. Excess blood sugar can damage nerves. You may notice tingling and numbness in your hands and feet, as well as painful burning sensations in your hands, legs, and feet.
- Red, swollen, sensitive gums. Diabetes can reduce the ability to fight microbes, increasing the risk of gum infection and the bones that hold teeth in place. Teeth become loose and inflammation can occur, especially if you have gum infections before diabetes develops.
Type 1 diabetes usually develops quickly, so its symptoms are more pronounced. The second type often does not cause any unusual problems because it develops gradually and in a very subtle way over many years. It is diagnosed only after the complications of diabetes are detected. If you notice any possible early signs of diabetes, talk to your doctor. The condition is diagnosed earlier and treatment can begin earlier.
4 causes of diabetes. What does it come from?
- Heredity. The tendency to diabetes is transmitted directly to the offspring, and the manifestation of the disease can also depend on other factors during life, and this is the reason why diabetes does not occur in every offspring. There are numerous examples of this behavior of diabetes in everyday life. It is known that children of parents should not suffer from diabetes. In addition, diabetics themselves are not always closely related to the onset of this disease, or they do not know the medical history of their deceased predecessors.
- Other diseases and conditions. Unlike hereditary diabetes mellitus, there are diseases and conditions in which diabetes can be diagnosed. Such diabetes is called secondary because it develops under the direct influence of a real disease or a harmful effect on the functioning of the organism. What causes diabetes mellitus? The occurrence of the disease is possible with chronic alcoholism, chronic diseases of the pancreas, various endocrine disorders (adrenal glands, pituitary gland, thyroid gland), obesity and other conditions. The appearance of diabetes in these conditions and diseases is associated with impaired breakdown of glucose in the blood under the influence of the same causes that led to the development of this disease or condition.
- Additional risk factors. In addition to the hereditary transmission of the disease, there are other causes of diabetes, such as a diet rich in sweets, fat intake and obesity, reduced physical activity, transition period in men and women (menopause), tendency to frequent infections, colds and inflammations. It is also known that risk factors for the onset of diabetes in the modern lifestyle include changes in the environment, lifestyle and diet (rural - urban), performing professional jobs that require a high mental load (stressful situations), giving birth to a large child (more than 4 kg)and others.
- Effects of certain medications. The first group of drugs that can affect the external manifestation of diabetes include drugs used for rheumatic diseases, chronic respiratory diseases, some drugs for kidney and skin diseases, and various allergic diseases. Another group of drugs are products that work on blood pressure and better urination. In addition, oral contraceptives or birth control pills have an effect on the behavior of blood sugar. There are other drugs and hormones that affect the development of diabetes. But all these drugs are known to medicine and control of their intake allows timely elimination of disorders in the behavior of blood sugar.
Diagnosis of diabetes
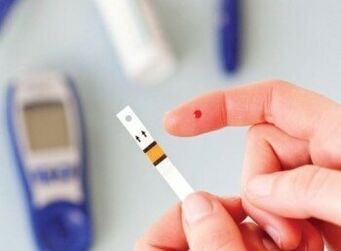
The diagnosis of diabetes mellitus is carried out in the laboratory. The doctor confirms (or refutes) the diagnosis based on the following data:
- If in two cases the fasting blood glucose level is higher than 7 mmol/l
- If blood glucose at any time of the day is greater than 11. 1 mmol/L
- Your doctor may order a so-called glucose tolerance test (OGTT). This test measures fasting blood sugar and then, after drinking a drink, a sweet liquid consisting of 75 grams of glucose dissolved in water. Measuring blood sugar confirms the diagnosis of diabetes.
Blood glucose levels can be higher than normal (6 to 7 mmol/L glucose, or between 7. 8 and 11. 1 mmol/L 2 hours after a glucose tolerance test) and even lower than the level at which diabetes is diagnosed. A diagnosis of impaired glucose tolerance or prediabetes can be made.
How to treat diabetes?
Diabetes can be treated in several ways:
- insulin and diet;
- pills and diet;
- one diet;
- Combined insulin therapy + pills (is a very common way for type 2 and obesity, insulin and metformin are taken.
There are 5 basic principles of diabetes management. The choice of treatment method depends on many factors.
The choice of treatment depends on:
- age (children and younger adults always receive insulin and diet)
- complexity of the disease (decrease in insulin production or complete absence of synthesis in the pancreas)
- physical condition (fat, thin or normal weight)
Prevention of diabetes
Prevention of type 2 diabetes involves an individual approach - counseling on the implementation of simple measures that will lead to a change in lifestyle. You must change your diet, maintain physical activity, control your body weight, stop smoking and use medications only as directed by your doctor.
Changing the way of eating means eating foods according to energy needs, optimal food composition, understanding what can be eaten without restrictions, foods that contain a lot of simple sugars, cooking food, the influence of physical activity on energy consumption.
Physical activity should become a habit. Your daily physical activity schedule should include:
- At least 30 minutes of walking a day.
- Use the stairs instead of the elevator.
- Walk or bike to work.
- When using transportation, get off early and walk the rest of the way.
- Walk to shops and other amenities.
- Supervise children in their physical activity.
- Clear the snow and organize the garden.